Team Members: Dr.P.Subashini, CMLI Coordinator,Professor of Computer Science.
Dr.M.Krishnaveni, CMLI Co-coordinator, Assistant Pofessor(SG), Departemnt of Computer Science.
Dr.A.Dhanalakshmi, Associate Professor of Computer Science, Gobi Arts and Science College.
Dr.R.Janani,Research Assistant,CMLI.
Ms.Tamil Purani T, II MCA , Gobi Arts and Science College.
Project Summary:
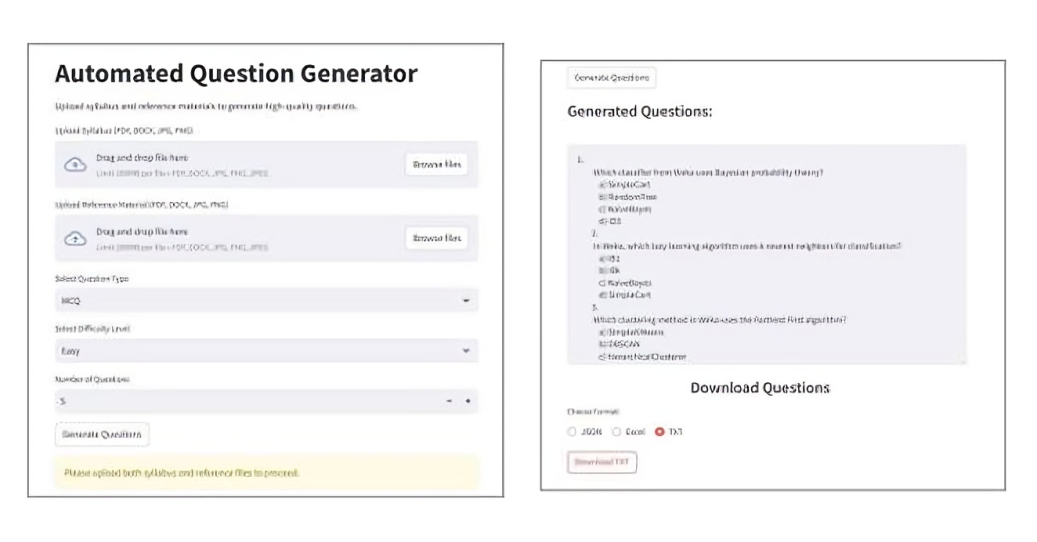
The Project entitled “QUESTION BANK GENERATION TOOL USING LARGE LANGUAGE MODEL” to develop an AI tool that generates customized questions based on syllabus content and reference materials, offering both MCQ and open-ended question formats with specified difficulty levels. Traditionally, creating question banks was a difficult and time-consuming process. Examining the curriculum, textbooks, and reference materials to identify crucial ideas and significant themes was the responsibility of educators and subject matter specialists. In order to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the subject, this technique involved deliberately constructing questions with varying degrees of difficulty. Teachers must carefully craft these questions to guarantee a suitable balance of various types, such as essay-style questions, multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and short-answer questions. To guarantee that the questions were precise, understandable, and consistent with the learning objectives, this manual approach required a great deal of work, careful planning. Additionally, in order to guarantee the quality and applicability of the question bank, teachers frequently had to work together and conduct several reviews. This manual approach frequently resulted in mistakes, inconsistencies, and gaps in topic coverage despite their best efforts. The method became even more complicated when handling massive amounts of content, especially from comprehensive reference materials. The need for a quicker, more effective way to produce high-quality question banks became apparent as educational demands increased. The Question Bank Generation Tool overcomes these challenges by utilizing technology to automate and improve the question creation process. With the use of this program, users can upload reference materials and syllabus documents, which are then examined to extract important details that will help create thoughtful and organized questions. By choosing the question type (MCQs, 5-marks, 10-marks), the desired level of difficulty (Easy, Medium, Hard), and the required amount of questions, users can customize their preferences. The tool evaluates the uploaded content intelligently, extracts important details, and creates insightful, well-structured questions that correspond with the reference and syllabus materials. To preserve quality and relevance, the algorithm makes sure that the variety of question kinds and levels of difficulty is balanced. The questions appear for review on the internet when they are generated. Additionally, users can choose to download the created 2 questions in JSON format for convenient access and use into learning materials. The Question Bank Generation Tool ensures that clear, correct, and syllabus-focused questions are created while decreasing human effort by integrating automation with a user-friendly web interface. This solution is intended to help content creators, institutions, and educators create efficient and efficient question banks. To ensure both accuracy and efficiency, the Question Bank Generation Tool is developed using a systematic method. The web platform is designed with a user-friendly interface that allows users to log in, upload syllabus and reference materials, and specify their preferences for question type, difficulty level, and quantity. The system preprocesses the submitted content after submission by removing unnecessary language and extracting important information. Based on the inputs supplied, the refined model then produces insightful and well-structured questions. The output is refined using post-processing techniques to guarantee relevance, coherence, and clarity. The generated questions are then presented for review on the website, where users can also choose to download them in JSON format for convenience.